|
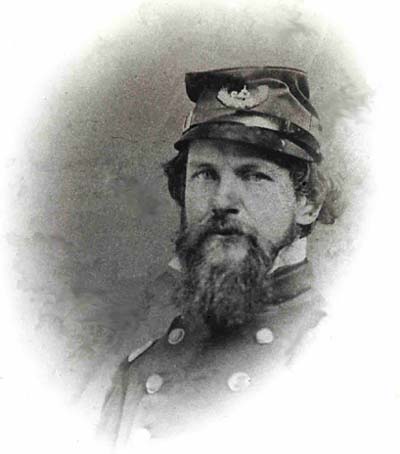
Colonel Roderick N. Matheson: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
urHealdsburg.com |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Colonel Roderick N. Matheson: City Builder and Civil War Hero
Roderick Matheson, for whom the broad, cherry tree-lined street in Healdsburg, California is named, was a strikingly handsome man possessed of intelligence, seemingly limitless energy, optimism, and political ambition. He was also an incurable idealist and passionate patriot, two qualities that would in the end prove fatal. Like an unerring missile, the short trajectory of his life intersected with some of the most important events in the history of California and the nation. That trajectory also brought him to the infant town of Healdsburg in the 1850's. It was here that he had his most permanent home and here that his body, finally restless no more, was buried. It is fitting that it is here that he is remembered best. Roderick Nicol Matheson was born in Inverness, Scotland on May 28, 1824. At the age of 15 he emigrated with his parents, Thomas and Jane Nicol Matheson, to America, settling in New York City where his father became a businessman. Finishing his education in the bustling metropolis of New York, Roderick married the daughter of an old New York Quaker family, Maria Antoinette Seaman, on the last day of the year 1844.[1] The young couple moved shortly after their marriage to Cleveland, Ohio where Roderick sold real estate. Here too at least one child, their firstborn Emma, died in 1845. Returning to New York, Matheson became associated with a large importing house for a short time, and then settled in as a school teacher, a vocation he would keep to the end of his life.
Journey Around the Horn In early 1849 Roderick contracted Gold Fever, and became part of the first wave of adventurers to reach California via Cape Horn in 1849. He left New Jersey on board the ship Pacific on January 22, 1849. The voyage was lengthy and difficult, but Matheson's insightful, humorous, and highly descriptive letters written home to "Netty", as his wife was always known, are a pleasure to read. A near mutiny during the second month of the voyage prompted Roderick, a natural leader, to organize a group of passengers into the "First Brigade of Wolverines". The Wolverine's deckside drills to protest the ship captain's orders seem comic as related by Matheson, the cause of the revolt being the quality of food served.[2] At one point in very real danger, the vessel was forced to dock in South America to avoid shipwreck. Matheson's letters show the frustration and anxiety of the gold seekers on this mostly monotonous, six-month voyage, with no opportunity to communicate with loved ones. Matheson's native optimism is high at the beginning when he tells his understandably downcast wife, "Dear Nett you must keep up your spirits. Look forward to the time that I shall return with a Pocket full of Rocks."[3] As the dull days plod on however, he admits, "You cannot imagine the amount of anxiety I labour under here. I am not only shut off from all communication with those we hold most dear upon earth, but we are also in suspense as regards our enterprise. O! what would we not give to have just the news that the account from California was as encouraging as it was when we left New York."[4] Referring to the fastest time that mail could travel to his home in New York, Matheson glumly inquires (mostly to himself), "What is the use of asking questions that take six months to answer?"[5]
The "Portable" City of San Francisco Becalmed again and again as his ship approached the harbor at San Francisco the frustration of the voyagers was released in a long, loud burst of "huzzahs", as the wind finally cleared the fog and revealed that legendary golden land.[6] When Matheson finally set foot in the raucous vital town of San Francisco he seemed bewildered:
"It is a little ahead of anything that I have seen yet. It is built upon a hill of sand. I say built; I should say placed, for the tenements are mostly of canvas. A slight wooden frame with canvas stretched upon it. They charge $50 for the privilege of pitching a tent in the boundaries of the city. But we have selected a very pleasant little valley with high hills on one side and the harbour in front. Tomorrow we take possession of it. We have named it Excelsior Valley."[7]
Roderick and his sailing companions were at first very nervous about the theft of their belongings, but soon relaxed. "...I never was in a place where I have seen so much property exposed in the open. The streets are lined with goods, the wharves or landings are in the same condition. My trunks have been out ever since I have been here...there is no more fear of anyone taking anything, for every person has more than he knows what to do with. If a man wants a clean shirt, he can buy one cheaper than he can get it washed. If anyone is caught stealing, he is either shot or has his ears cut off and whipped."[8]
Less than a month later Matheson marveled, "Only to think that a few months ago this was a wilderness and the place where now stands the portable city of San Francisco was occupied by a few mud huts. I can scarcely believe my own eyes that I am in the same place where I landed a few weeks ago. For the City has three-fourths of it been built since I came here or perhaps I ought to say, put up; for the present City was built in the United States and China and floated around the Horn or across the Pacific. [Matheson refers to pre-fabricated buildings]. Talk about Aladdin's wonderful lamp, and wonder ye who have never seen a California city rush into existence."[9] Matheson lasted only a short time at the mines; his real gold lay in the infant town of San Francisco, which he adopted wholeheartedly. His native talent soon brought him prominence, and he seemed to become involved in any project that furthered the interests of that city.
He helped to organize the Mechanic's Institute in San Francisco, a training school, and became its president. In 1852 he was appointed Comptroller of the City of San Francisco. He was an active member of the fire department, one of the founders of the vigilant Engine Company No. 9, and a member of the Marion Rifles, a local militia. In 1854 he was appointed a general of a division of the Mexican Army, and resident commissioner of Mexico in San Francisco. As Commissioner he contributed greatly to better relations between the United States and Mexico. His Mexican Commission was confirmed by Juarez, then Chief Justice of Mexico, and was still in effect at the time of his death.[10]
Matheson's Home in the Country Perhaps tiring of the increasing lawlessness in San Francisco, perhaps looking for a quiet place to raise his children, Matheson moved his family to Healdsburg in 1856. That family now included his wife, Netty and his son, Roderick, Jr. (born in 1849 while his father was en route to California), and brother-in-law Jesse Seaman. These three had joined Roderick in San Francisco in 1853, and apparently lived with him at Washington and Leavenworth Streets in the Nob Hill section. Jesse served as a Matheson's clerk in the Comptroller's office. A daughter, Maria Antoinette was born in 1855.
When they moved to Healdsburg in 1856 Roderick and Jesse Seaman purchased 900 acres adjoining the east side of town, and set about becoming farmers. Within a year Matheson established one of the first and most interesting of Healdsburg's early festivals, the May Day celebration and jousting tournament, first held on the part of his land now known as Oak Mound Cemetery. On May Day amid the mighty oaks, participants, dressed as medieval knights, tried to spear wooden rings with long lances while on horseback. Matheson and two other local businessmen, William M. Macy and Ransom Powell, would later donate that same land and lay out the cemetery for public use.[11]
Although Matheson may have envisioned an idyllic country life and himself a gentleman farmer, Jesse Seaman probably did most of the farming. Roderick reverted to a former vocation, that of schoolteacher. Matheson taught in the first school built in Healdsburg, the Russian River Institute, beginning in March of 1858. Matheson had been instrumental in the building of that school, having donated part of the land on which it was built in 1857. In 1859 the Institute was taken over by a group of local citizens headed by Matheson, re-opening shortly thereafter with the impressive title, The Agricultural and Mechanical University of California. Matheson not only taught in the school, but was the principal. At least some of the students paid for their education by working on the Matheson farm. Since that time the street fronting the old school has been called University Street.
Matheson and the other board members had great ambitions for the school, envisioning a mechanical shop, a mill, student worked corn and hemp fields, and botanical gardens. Matheson and another board member, Charles E. Hutton, had even secured the use of a printing press owned by local citizen, J.B. Boggs, and had gathered $400 in local subscriptions to support a newspaper to be published by the college. [12] Yet they were beset by financial problems in their ambitious endeavor. Individual board members "invested" more and more of their own money to keep the school in operation. Still, the idealist Matheson wrote a strong letter to the board on Sept. 7, 1860: "...All institutions of a literary and scientific character, that have any prominence in the world, unless endowed by the dying millionaire or royal bequest, have had, in their infancy to struggle for very existence; and had there been at the head of their affairs, a weak, vacillating and timid Board of Directors, they must have perished ingloriously, and have sunk into obscurity..."[13] Called to Washington Only four months after Matheson fired off this letter his attention was called away to another, much brighter lit arena. Always active in politics, Matheson had become a member of the Free Soil Party, which was intent on keeping slavery out of California and Oregon. President-elect Abraham Lincoln invited Matheson to attend his inauguration in Washington D.C. because of this association in January, 1861. Following the March 4th inauguration Matheson was one of five men summoned by Lincoln to discuss California appointments. His letters home to Healdsburg make it clear that Matheson expected to be in Washington only a few weeks. During this time he had several interviews with Lincoln and Matheson had high hopes that he would "get a position in some lucrative office...in San Francisco."[14] Although he referred to the capitol as the "dullest of all places", it is clear that he enjoyed exercising his considerable political skills. "I have been as busy as a bee in a tar bucket and happy as a clam in high water for I have had no time to think of home except for a minute at a time. My whole energies have been directed towards Polyticks."[15] As he had earlier in San Francisco, Matheson began quickly to absorb the mood of Washington, D.C., and became embroiled in the political machine that was daily sending out ever more ominous threats of civil war. In one of his letters home to Healdsburg, he expressed the hope that appointments would be made the following day, leaving him free to return to his family. "Yes, home where my Netty awaits me, where my dear children are looking for their Pa, where my hopes, expectations, desires, and future happiness all center..."[16] Matheson had fathered two more children in Healdsburg, only one of which survived infancy. This was "Baby George", born in 1860 not long before Matheson left Healdsburg. It became obvious to Matheson that political appointments would be delayed, although he remained optimistic, stating, perhaps to placate Netty, "I expect to make a handsome thing out of my employment in public business."[17] Civil War Colonel
In April 1861 there is a sudden break in Matheson's correspondence home. Instead of making the long-anticipated appointments in April, President Lincoln, with war imminent, asked for 75,000 loyal state militiamen to serve for three months. Irretrievably swept into the whirlwind of passions and politics of the mounting national crisis, Matheson immediately volunteered and was soon elected Colonel of the 32nd New York State Volunteer Infantry, organized on Staten Island on 31 May 1861. Because of its California connection, Matheson and others commonly referred to this regiment as the First California Regiment.
Matheson led this regiment in the first major battle between the states, the Battle of Bull Run. His troops had the responsibility of protecting the rear of the Union Army near Centerville, Virginia, about seven miles from the main engagement at Bull Run. For his actions he won a commendation from President Lincoln himself, and achieved the only Union victory of the day in that skirmish.[18] In one letter home Matheson displays his frame of mind and makes one of many arguments to his wife, justifying his abandonment of his family and military enlistment: "I am back from battle with my reputation for a good soldier being established. I am held in high estimation by my men and officers, by all the Regt. around. Netty, my love, what would I do or give if you were by my side, that I could look into your face and get your approving smile for trying to fight and sustain YOUR country and now mine. Do you not think I may, by and by, rank as an American?..."[19] In another letter from Alexandria, Virginia, written October 11, 1861: "Have I said too much? Out of the heart the mouth must speak or the heart breaks. O my Netty, my darling, you know not how miserable your poor husband is, in this far off country of contention, discord, and strife. this is not the land I left 12 years ago everything is changed but such a change not, by any means, for the better but the worse. Your once boasted country is falling to pieces and destruction. The land of my children is imperiled, her liberties are about to be subverted. My country by every tie that can be held holy, sacred and assumed is assailed. Would you as a woman, an American proud of your revolutionary descent, have the man of your choice prove himself unworthy of your alliance, prove reticent to duty, a coward! No, I think I know my Netty better."
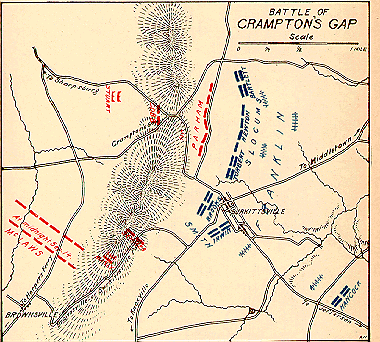
As the war continued the First California Regiment, now about 1,000 men led by Colonel Matheson, engaged in one bloody battle after another often disheartened by defeat and lack of supplies. After defending Washington D.C. until March, 1862, Matheson's regiment headed south with the Union Army towards Richmond, Virginia, the capitol of the Confederacy. Matheson's regiment fought in most of the actions preceding the assault on Richmond and covered the retreat of the Union Army back to Centerville. Much of this fighting took place in insect infested, disease-ridden swampy areas. It becomes clear from Matheson's correspondence that Netty was unhappy in Healdsburg. She was deeply troubled about falling into poverty, and desperately wanted Matheson to resign his commission and reunite with her. Plans were even underway to sell the Healdsburg farm and have Netty join Roderick in New York. Although he agrees with her decision to abandon the place, he seems to retain a fondness for it, recalling, "the debating society May Day festivals Military Companies Specimen hunting Political excitement all the things that went to make our Patmos or exile in the Country tolerable."[20] [Note: Patmos was the Greek Island of exile where John the Evangelist wrote the Book of Revelations - Matheson was nothing if not classically educated!] Later he says of their farm in Healdsburg, "...it is a pretty place it is a Sensible place it is all that a man or woman could wish for yet to you or me or our family it is of no use..." In April, 1862, he assures her that as soon as the Union forces take possession of Richmond, and victory is assured, he will resign.[21] In July 1862, Colonel Matheson and his troops had time to rest for a short time. It was at this point that Matheson had hopes of becoming a general, an appointment for which he was well qualified, and one that might have stationed him on the Pacific Coast, nearer his family. His dream was to make his wife and children, and perhaps the whole nation, proud of him. By serving his country he had won the right to send his son, Rody, to West Point, a thing that would have, "...paid me for all I have born."[22] Matheson Returns Home From September 2 to September 14, 1862, the Union forces engaged in a series of skirmishes, one of which stormed a Confederate stronghold at Crampton's Gap on South Mountain. As Matheson led his regiment on an assault up the mountain, a miniball struck his right thigh. He was evacuated to a field hospital at Burkittsville, Maryland. A later investigation stated that ..."the wound was not considered serious, the leg was not amputated, and Colonel Matheson did not himself, nor did his friends apprehend any danger." Yet on October 1st Colonel Matheson began to bleed severely. He died the next day at the age of 38. Matheson's Corp Commander, General W.B. Franklin wrote that the Union lost "one of its best Colonels", and a great deal of fuss was raised about how and why he was allowed to bleed to death in an army hospital. Matheson's body was taken to New York City, where it lay in state in the Governor's room at City Hall until Oct. 9th. On that date an imposing military funeral was held at the Green Street Methodist Church in New York, where he and Netty had been married 18 years before. Many notable men served as pallbearers including Generals John C. Fremont (then a U.S. Senator from California) and John S. Ellis; and C.K. Garrison, who had been Mayor of San Francisco in 1853. California's senior senator and Rod's old friend from his days in San Francisco, Alexander McDougall, presided over the services. Later the remains were transported by ship across the Isthmus of Panama, arriving in San Francisco aboard the steamer Sonora, on November 6. Here it was met by the First California Guard. The Healdsburg band led a torchlight procession into San Francisco, playing a slow and solemn funeral dirge. Matheson's body lay in state in Platt's Hall and another funeral was held. Once again, many notables attended including then Governor of California, Leland Stanford, and the founder of the Bank of California, William Ralston. Finally, what remained on earth of Colonel Roderick Nicol Matheson was put aboard the steamer Petaluma, to be met in the city of that name by the Petaluma Guard, the Emmet Rifles, the Santa Rosa Military Company, and the Sotoyome Guard of Healdsburg, of which Matheson had been a member. At last this frail form, minus the ambitious, idealistic spirit that once animated it, was taken by wagon to Healdsburg and put to final rest at Oak Mound Cemetery November 9, 1862. Epilogue
Rody, the son that Colonel Matheson so wanted to attend West Point, never attended that academy. He was killed in a threshing machine accident at Davisville near Sacramento on July 27, 1870. Matheson's wife, "Netty" was awarded a widow's pension and lived the rest of her life on the Healdsburg farm. She died there in 1884. "Baby George" was killed in November, 1887, at the age of 26. Marie Antoinette, always known as "Nina", Matheson's only surviving daughter, lived in Healdsburg for many years, marrying a prominent local rancher's son, Jirah Luce. They enlarged and remodeled the old Matheson home at 751 South Fitch Mountain Road in 1904. Nina Matheson Luce died in 1920. Roderick Matheson's granddaughter, Nina Rose, lived in Healdsburg all her life, and his great granddaughter, Nina Von Tillow, lived in Healdsburg until just before her death in 1995. [This home, known in later years as the George Warfield home, has been restored by the current owners, Ralph and Judy Jenkins. --- This sentence soon to be updated circa 2003. ] |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||











 A
number of skirmishes occurred on Sunday, September 14, 1862 in the same
area and are known as "The Battle of South Mountain". Some historians
believe that it is more accurate say "The Battles on South Mountain."
Nearby, to the northeast, the
Battle of Antietam took place three days later, resulting in the deaths of
23,000 men.
A
number of skirmishes occurred on Sunday, September 14, 1862 in the same
area and are known as "The Battle of South Mountain". Some historians
believe that it is more accurate say "The Battles on South Mountain."
Nearby, to the northeast, the
Battle of Antietam took place three days later, resulting in the deaths of
23,000 men.