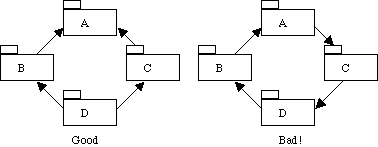
Ideally, the dependency graph should move from most stable to least stable packages to minimize the amount of changes introduced.
A package makes a good unit of release (individual classes are generally too granular). If there are cyclic dependencies, a change in any package in the chain forces all packages to possibly change. In the "bad" scenario depicted below, if package C were to change, package A would have to change because it depends on C. However, package B would have to change because it depends on A, and package D would have to change because it depends on B. Imagine how bad this could get if each package were owned by a different developer. In the "good" scenario depicted below, if package C were to change only package D might need to change.Base classes should be abstract.
Ideally, the dependency graph should move from most stable to least stable packages to minimize the amount of changes introduced.
Things that are not stable should not be heavily depended on. An inheritance relationship is a heavy dependency relationship, so the base class that is depended on should be very stable, therefore abstract. Unstable classes have many implementation details that are likely to change, so they are concrete classes.When in doubt about whether to add something to an interface, don't.
In general, it's much easier to add something to a class or interface than to root out something that other classes may have become dependent upon.
It is a common mistake to confuse == and equals(). In general, equals() is preferred for objects since it defaults to a reference comparison (==) but may be overridden. If you are going to override equals(), think about overriding hashCode(), which is used in collections.Use an explicit serialversionUID for serializable classes.
If classes are serializable, it makes sense to explicitly define a serialversionUID so that you can control version compatibility of serialized objects. If you don't define a serialversionUID, you get a default compiler generated hash which (1) is generally unintelligible and (2) can change even if you make a "compatible" change as defined by the serialization spec. I think of a serialversionUID as a version number and just use values like 1L, 2L, 3L, etc.Don't use \n in String objects that are subject to file I/O.
New line characters are handled differently on different platforms. Unfortunately the file I/O classes don't want to perform automatic conversions on newlines, so using PrintWriter may produce the wrong output, or output that works on one platform but not another. Use PrintWriter.println("sometext") instead of PrintWriter.print("sometext\n"), or if you need to embed newlines replace the \n characters with the line.separator property.Put preference files in the directory specified by the user.home property.
It goes without saying that one shouldn't assume the existence of a particular directory structure.When using JDBC, remember that JDBC indexing starts with 1, not 0.
Unlike Java array indexing, ResultSet column indices start with 1 and not 0.Be sure to configure rmiregistry properly when distributing an application using RMI.
A common problem is to get a ClassNotFoundException which occurs when a client class cannot obtain a stub from the server. Many of these problems are due to rmiregistry either not being able to find the stubs in itsclasspath (as opposed to the server's classpath) or not having the proper java.rmi.server.codebase property set up.Use JUnit for white box unit testing.
It will save a lot of trouble. Do it.